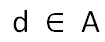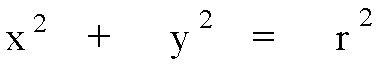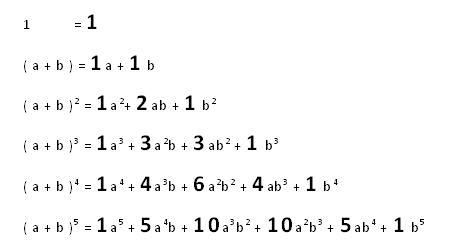動態規劃
1. 大問題可以分解為子問題
2. 每一個子問題的答案可以被儲存起來 供下次直接取用 不必再重新計算
finalfrank 發表在 痞客邦 留言(1) 人氣(2,711)
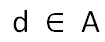
Let A sequence of number be
A1,A2,…..,Ai,…..,An in an increasing order
N is the number of elements
finalfrank 發表在 痞客邦 留言(0) 人氣(578)
Multiple Loop To Recurrence Function
finalfrank 發表在 痞客邦 留言(0) 人氣(3,107)
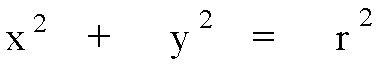
割圓術到底能不能算出無限位數的 pi π呢......?
首先呢,我們要先知道圓形的一個公式
Here's the formula of a round.
其中, r 是半徑
r is the radius of the round.
運用這個公式,我們可以求得在一個圓形上出現的所有座標
Using this formula, we can get all the positions of the round.但是可想而知,如果圓上面,每個座標都要求到...
其實是有無限多個!
所以,我們就把顯示座標限制在
_____ _____
( √整數 , √整數 )However, the number of the positions on the round...is infinite..So, we just show the positions that are square roots of integers.
_____ _____
( √Integer, √Integer )
finalfrank 發表在 痞客邦 留言(0) 人氣(1,101)

可以一次計算多個數值的最大公因數 最小公倍數
[ 按此下載 ] [ English Version is Available ]程式碼 (僅供學習參考用) :
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int lcm(int a,int b);
int gcd(int c,int d,int e);
int main(void)
{
int g=1,get[10],c,re,re2,re3,gcd2,k;
printf(" 《最大公因數、最小公倍數 計算機》 \n");
while(g=g)
{
while(g==g)
{
printf("\n請輸入第 %d 個數值 ,輸入 0 開始計算: ",g);
scanf("%d",&get[g]);
gcd2=get[g-1];
if(get[g]==0)
break;
g++;
}
g--;
for(k=1;k<=g;k++) /* 排序,從小的數值排到大的 */
{
for(int i=1;i<=g;i++)
{
if(get[k]>get[i])
c=get[k],get[k]=get[i],get[i]=c;
}
}
re=re2=get[g];
while(g>=2)
{
re3=re2;
re=lcm(re,get[g-1]);
re2=lcm(get[g],get[g-1]); /* 計算 這次 最小公倍數 */
re2 = gcd(get[g],get[g-1],re2);
gcd2 = lcm(re2,re3); /* 計算 這次 和 上次 最小公倍數 的 最大公因數 */
gcd2 = gcd(re3,re2,gcd2); /* 計算 這次 和 上次 最小公倍數 的 最小公倍數 */
g--;
}
printf("\n最大公因數 : %d\n\n最小公倍數 : %d\n\n=====================================",re,gcd2);
g=1;
printf("\n\n請輸入第 %d 個數值 ,輸入 0 離開程式: ",g);
scanf("%d",&get[g]),g++;
if(get[1]==0)
{
printf("\n");
break;
}
}
}
int lcm(int a,int b)
{
int c=b;
if(a<b)
c=a,a=b,b=c; /* a b 互換 */
b=a-b;
if(b!=0)
{
while(a%b!=0)
{
c=b;
b=a%b;
a=c;
}
}
else
b=c;
return b;
}
int gcd(int c,int d,int e)
{
e = c * d / e;
return e;
}Code ( for reference only ):
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int lcm(int a,int b);
int gcd(int c,int d,int e);
int main(void)
{
int g=1,get[10],c,re,re2,re3,gcd2,k;
printf(" < LCM & GCD CALCULATOR > \n");
while(g=g)
{
while(g==g)
{
printf("\nEnter #%d Value , Enter 0 to begin calculate : ",g);
scanf("%d",&get[g]);
gcd2=get[g-1];
if(get[g]==0)
break;
g++;
}
g--;
for(k=1;k<=g;k++) /* Sort, from small to big */
{
for(int i=1;i<=g;i++)
{
if(get[k]>get[i])
c=get[k],get[k]=get[i],get[i]=c;
}
}
re=re2=get[g];
while(g>=2)
{
re3=re2;
re=lcm(re,get[g-1]);
re2=lcm(get[g],get[g-1]); /* Calculate the lcm this round */
re2 = gcd(get[g],get[g-1],re2);
gcd2 = lcm(re2,re3); /* Calculate the lcm of the gcd of this round and last round */
gcd2 = gcd(re3,re2,gcd2); /* Calculate the gcd of the gcd of this round and last round */
g--;
}
printf("\nL C M : %d\n\nG C D : %d\n\n=====================================",re,gcd2);
g=1;
printf("\n\nEnter #%d Value , Enter 0 to exit : ",g);
scanf("%d",&get[g]),g++;
if(get[1]==0)
{
printf("\n");
break;
}
}
}
int lcm(int a,int b)
{
int c=b;
if(a<b)
c=a,a=b,b=c;
b=a-b;
if(b!=0)
{
while(a%b!=0)
{
c=b;
b=a%b;
a=c;
}
}
else
b=c;
return b;
}
int gcd(int c,int d,int e)
{
e = c * d / e;
return e;
}
finalfrank 發表在 痞客邦 留言(0) 人氣(8,943)
巴斯卡三角形
Pascal's Triangle
[ 演算程式 ][ Pascal's Triangle Computer ( English Version ) ]
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 00 1 2 1 0 00 1 3 3 1 00 1 4 6 4 1計算原理:如上面文字所列 每一格的數值即是( x , y ) ,其中 y 是由上往下數套入公式 ( x , y ) = ( x-1 , y -1 ) + ( x , y-1 ) 使用陣列,馬上就能寫出來Every number existed in the triangle can be expressed like ( x , y ) = ( x - 1 , y -1 ) + ( x , y - 1 )Please notice that the " y " here , is counted from up to down. ( For example : ( 2 , 1 ) = 0 ( 2 , 2 ) = 1 ( 3 , 3 ) = 3 )You can try to write a script to compute this triangle using the formula above. ( It's recommended to use array. )在數學上的應用:Usage of Pascal's Triangle in Mathematics
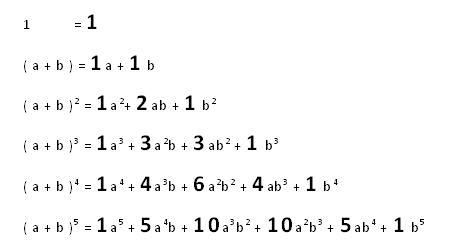 原始碼 (使用最省記憶、最有效率的寫法)#include<stdio.h>
原始碼 (使用最省記憶、最有效率的寫法)#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main ()
{
int phase[34][2],counter,x,row,y;
printf(" 《楊輝三角形產生器》\n\n本程式可以輸出你輸入的列數\n\n任何時候都可以輸入-1離開\n\n(32位元電腦只支援到34行)\n\n ");
while(x==x)/* 無限迴圈開始 */
{
for(x=0;x<=34;x++) /* 清空變數 */
{
for(y=0;y<=1;y++)
phase[x][y]=0;
}
printf("請輸入顯示列數 : ");
scanf("%d",&counter);
printf("\n");
if(counter>=35)
counter=34;
if(counter==-1) /* 使用者輸入 -1 離開 */
break;
phase[0][0]=1; /* 初始化計算用數值 */
row=1;
while(row<=counter) /* 程式跑到指定列數才結束 */
{
for(x=1;x<=counter-row;x++) /* 美化用的迴圈... */
printf(" ");
for(x=1;x<=row;x++) /* 計算並顯示數值 */
{
phase[x][1]=phase[x-1][0]+phase[x][0];
printf(" %d",phase[x][1]);
}
for(x=0;x<=row;x++) /* 放入這個迴圈的數值 讓下個迴圈計算 */
phase[x][0]=phase[x][1];
row++; /* 跑的列數 +1 */
printf("\n\n");
}
} /* 無限迴圈結束 */
printf("(c) NTPU CSIE 49571602\n\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
} Pascal's Triangle Code. ( White Texts Hidden Below, for your reference. ) (Using the most efficient method, which saves most memory that I've ever tried.)#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main ()
{
int phase[34][2],counter,x,row,y;
printf(" << Pascal's Triangle Computer >>\n\nThis program computes the number of line you requested.\n\nYou may exit any time by typing -1\n\n( A 32-bit computer is limited to display less than 34 lines. )\n\n ");
while(x==x)
{
for(x=0;x<=34;x++)
{
for(y=0;y<=1;y++)
phase[x][y]=0;
}
printf("For How many Lines would you like to Compute : ");
scanf("%d",&counter);
printf("\n");
if(counter>=35)
counter=34;
if(counter==-1)
break;
phase[0][0]=1;
row=1;
while(row<=counter)
{
for(x=1;x<=counter-row;x++)
printf(" ");
for(x=1;x<=row;x++) /* 計算並顯示數值 */
{
phase[x][1]=phase[x-1][0]+phase[x][0];
printf(" %d",phase[x][1]);
}
for(x=0;x<=row;x++)
phase[x][0]=phase[x][1];
row++;
printf("\n\n");
}
}
printf("(c) NTPU CSIE 49571602\n\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
finalfrank 發表在 痞客邦 留言(0) 人氣(4,112)